All You Need to Know About Nylon for 3D printing
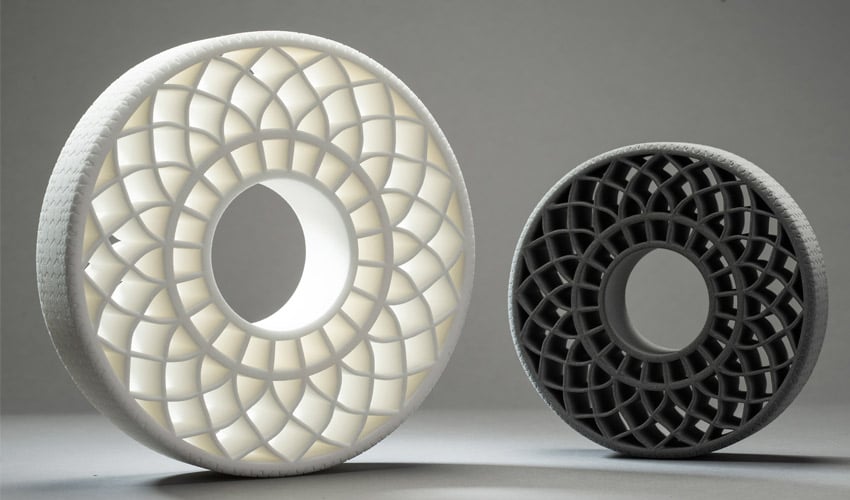

Nylon, also called Polyamide (PA) is a widely used polymer in the additive manufacturing sector. This thermoplastic is available in powder or filament form for technologies such as SLS, Multi Jet Fusion or FDM. These plastics are classified according to their chemical composition, and in particular according to the number of carbon atoms they contain – the most well known on the 3D printing market are undoubtedly PA12 and PA11, as well as PA6 for FDM. But what are the characteristics of nylon when used for 3D printing? Who are the manufacturers on the market and what are the applications? Find out more in our complete guide below!
Production and Characteristics of Nylon
Nylon first appeared in 1935 in the form of nylon 6.6. It was developed by Wallace Carothers who then worked for the chemist DuPont. This first material was patented in 1937, commercialized in 1938 and remains the most widely used today. Nylon is mainly found in the textile industry thanks to its flexibility and resistance. It was used in 1940 for the first time in the production of women’s stockings. Even in 3D printing, one of the most interesting characteristics of this material is its flexibility. Nylon 6, on the other hand, was first produced by Paul Schlack in the laboratories of IG Farben and patented in 1941. All other forms of nylon are later.
Nylon 6.6 (photo credits: BASF)
In addition to those already mentioned, two types of nylon are widely used in the industry: PA11 and PA12. What is interesting is that they are not only distinguished by a single carbon atom, but also have very different origins. PA11 is made from castor oil, a natural and renewable resource, while PA12 is made from petroleum. There is much debate about the origin of nylon and its impact on the environment. When they can, users choose PA11 over PA12 because of its good properties for skin contact items. But it must be said that even PA11 is not totally environmentally friendly, as there is often no place to recycle it, so it is thrown away like other types of plastic.
When it comes to 3D printing, it is important to note that nylon in powder form can be reused for multiple prints. In particular, the HP Multi Jet Fusion process is known to use polyamides such as PA12 and PA11, and to have a higher refresh rate compared to SLS technology. About 70% of the powder is not used during 3D printing, but is mixed with new powder to minimize waste.
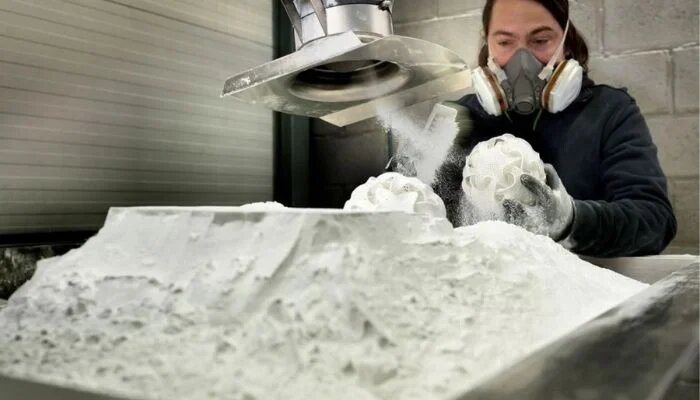

Nylon powder is widely used in additive manufacturing (photo credits: Materialise)
Nylon in 3D Printing
If we look at filaments, nylon is most often available with 6 carbon atoms, more commonly called PA6. It is a filament that has many interesting characteristics, including great flexibility, resistance to impact or abrasion. Additionally, its mechanical properties are quite close to ABS. However, note that nylon will require the presence of a heated plate inside the 3D printer (that can reach around 80°C) due to adhesion issues. It will also be necessary to take care of storage because it quickly absorbs the surrounding humidity (hygroscopic material) which could impact printing later. In terms of extrusion temperature, the 3D printer will have to rise to 250°C, or even 220°C for certain types of nylon. Nylon filaments are a good alternative to polycarbonate, as they are easier to print, more durable and ideal for printing parts requiring strength.
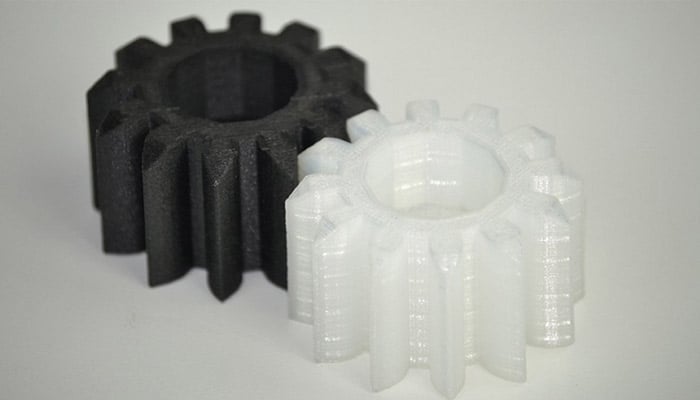

Photo Credits: Sharebot
When it comes to powder, the most commonly used Nylon is PA12. It is favored for its offers very high mechanical and thermal properties: it is extremely rigid, strong even at very low temperatures, stress resistant and has low moisture. In addition, it is easy to post-process (paint, dye, etc.). PA11 is also available in powder form and shares many of the same characteristics as PA12, but with some important differences. It has better thermal stability, light and UV resistance, and good elasticity. Parts printed with PA11 also have greater durability, making it an ideal material for producing functional prototypes or final parts with important mechanical properties. It is important to note, however, that PA11 absorbs more moisture than PA12.
Applications for Nylon in 3D Printing
Nylon is a very useful and versatile material. Its flexibility and strength make it ideal for automotive applications, such as the manufacture of friction and deformation resistant parts. It is also used in the manufacture of gears, hinges, and as a replacement for certain plastics used in injection molding. In addition, it is biocompatible, which means that it can be used to manufacture prostheses and other parts that will be in contact with the skin. Finally, it is a non-abrasive material, which makes it ideal for high use items and interior parts that tend to wear. It can also be easily painted to give it a more attractive appearance.
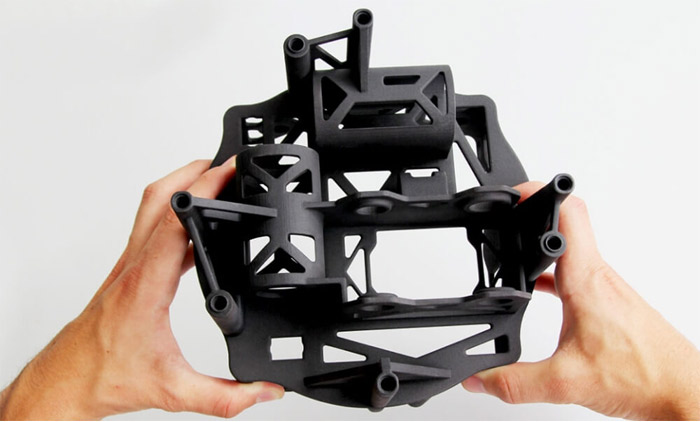

A part that has been 3D printed with PA12 (photo credits: Sculpteo)
The Main Manufacturers and Material Price
Major manufacturers of nylon filaments include Taulman3D, XStrand, Neofil3D, Volumic, Polymaker and machine manufacturers such as Zortrax, UltiMaker and Markforged. Note that nylon can be reinforced with carbon fiber or fiberglass for a higher performance composite material. In terms of price, for a classic spool (500 grams, 1.75 mm diameter) you should count between $25 and $40 depending on the brand; if you choose a composite material, the price can quickly climb to around $60-70. As far as nylon powder is concerned, the French chemical group Arkema is probably the largest producer of PA11 powder, marketed under the name of Rilsan PA11, since the 1950s. The German company BASF, which also produces PA6 and PA6.6, is also an important player in this market with its Ultrasint brand, which is compatible with HP Multi Jet Fusion machines and some SLS printer models.
For PA12, the manufacturers are Arkema and Evonik, while EOS, 3D Systems or Farsoon offer their own powders developed in collaboration with chemical companies. There are also polyamide powders filled with carbon fibers, Kevlar or glass beads. This is the case of HP 3D High Reusability PA 12 Glass Beads which, as its name suggests, is a thermoplastic filled with 40% glass beads and is characterized by its high reusability. The price of one kg of PA11 or PA12, standard or reinforced, varies from 100 to 200 euros, depending on the composition.
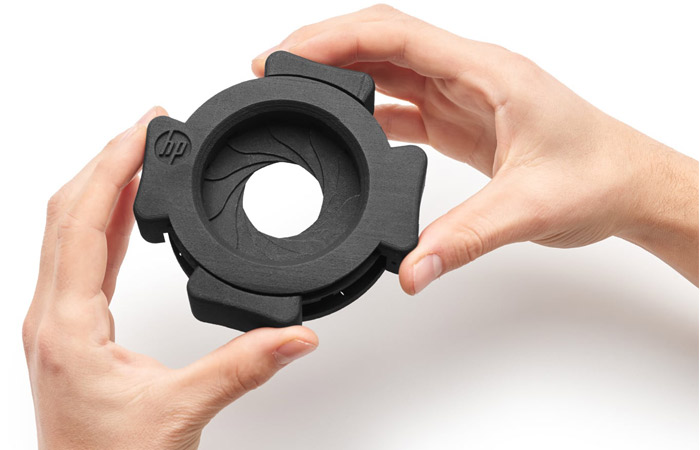

Photo Credits: HP
Have you used nylon for 3D printing? Let us know in a comment below or on our Facebook and Twitter pages! Sign up for our free weekly Newsletter to receive all the latest 3D printing news straight to your inbox!








Evonik is a world leader in the production high performance polymer powders, which have been used in 3d printing for over 20 years. The specialty chemicals company offers a wide range of nylon powders like PA 12, PA 613 or PEBA suitable for various 3d printing technologies.
Vous ne parlez pas de l’Onyx et composites de chez markforged, qu’en est il?
Recently i write an article about nylon filament and i got huge information from this post. You easily describe about polyamide filament (which is the chemical name for nylon). Thanks for your contribution in 3D printing industry. as a 3D printing exhaust, i like your contribution very much.
Recently i write an article about embroidery machines and I got information from this post. You easily describe polyamide filament (which is the chemical name for nylon). Thanks for your contribution in 3D printing industry. as a 3D printing exhaust, I like your contribution very much.
That’s one of the best nylon 3D printing guide. I looked at several forums and communities but found this content a great help. I just wanted to say thank you & keep it up.
Best 3d blog I have ever seen
Best guide to know about 3d printing
Medical billing, coding & credentialing services by MedICD are not just another billing solution to outsource medical billing and transcribe patient data into billing codes. An expert team of medical billers and coders at MedICD ensures timely preparation of the claims and expedite the overall process to ensure that medical practices get maximum reimbursements in less time.
It’s been a long time since I read such a good article, you write very clearly, easy to understand and really helpful for everyone, thank you very much.
Best 3d blog I have ever seen
visit our site: https://medicd.com/
3D printing in construction streamlines processes by enabling rapid prototyping, customization of components, and construction of complex structures. It enhances estimating accuracy through digital twins, reduces material waste, and contributes to cost efficiency, showcasing its potential to revolutionize the industry.