A Complete Guide to Aluminum 3D Printing
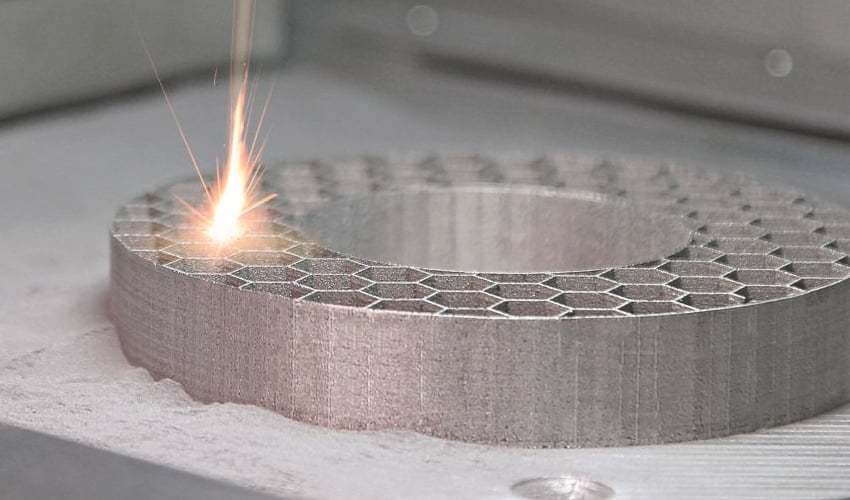
Aluminum is one of the most popular metals in the field of industrial production and, more specifically, in additive manufacturing. It is a strong, lightweight metal alloy that offers an ideal combination of mechanical and thermal properties. Companies involved in materials development, especially for additive manufacturing, offer a wide variety of aluminum alloys intended for metal 3D printing. These materials are truly versatile and offer a multitude of benefits depending on the properties required for each application. To better understand the properties of this metal and the benefits it brings to 3D printed parts, we took a closer look in this complete guide.
Material Characteristics
Aluminum (Al), with atomic number 13, is a chemical element present everywhere in the earth’s crust. It is a non-ferromagnetic metal, i.e. it cannot be magnetized by a magnetic field. Many of the aluminum alloys available for additive manufacturing consist of a combination of metallic and metalloid elements, including aluminum, silicon, magnesium or copper. Some of the most popular aluminum alloys are:
- AlSi7Mg – Aluminum with silicon (7%) and magnesium alloys
- AlSi10Mg – Aluminum with silicon (10%) and magnesium alloys
- AlSi12 – Aluminum with silicon alloy (12%)
- AlSi9Cu3 – Aluminum with silicon alloys (9%) and copper (3%)

Photo Credits: GE
The raw material from which aluminum is extracted is the mineral known as bauxite. To obtain aluminum, bauxite is first transformed into alumina by the Bayer process, and then the aluminum is extracted by a process called electrolysis. In addition to being a light metal with a low melting point, aluminum is a very good electrical and thermal conductor. The industrial use of aluminum has made it one of the most important materials, both in terms of quantity and variety of uses. Let us now see how this metal is used in the field of additive manufacturing.
Aluminum 3D Printing
When it comes to creating 3D printed parts with aluminum, there are a number of different methods to do so. One of the most widespread technologies for metal additive manufacturing is Laser Powder Bed Fusion (LPBF), in which a laser fuses point by point the metal layers that are spread on a powder bed. Within this same family, we also find Electron Beam Melting (EBM) technology, with the difference that the energy source is an electron beam instead of a laser.
In addition to these two, there are other metal fabrication methods capable of printing with aluminum, such as binder jetting, cold metal fusion and wire arc additive manufacturing (WAAM). Finally, we can find, although to a lesser extent, the use of aluminum with FDM technology. Although this method mainly works with plastic filaments, some companies have developed solutions compatible with this technology to create more resistant parts.
Aluminum 3D printed parts have a number of advantages and disadvantages over other metals. Among the benefits, aluminum is a high-performance material that offers interesting mechanical and chemical properties. In addition to allowing the fabrication of complex geometric structures, it has a high strength-to-weight ratio and is weather resistant. However, aluminum 3D printed parts are less rigid than those made with steel. Moreover, unlike titanium, aluminum is not a biocompatible metal, so it is not the ideal choice for use in the medical sector, as we will see below.

Aluminum is one of the metals with the best strength-to-weight ratio
Upon completion of the 3D printing process, the vast majority of aluminum parts require certain post-processing steps. This is mainly due to the fact that many of the technologies compatible with this metal are part of the powder bed family. Thus, one of the first processes to be carried out will be the removal of excess powder and fabrication supports, if they have been used.
In addition, the parts usually come out of the machine with a noticeable surface roughness, which is usually higher than with other powder materials. To obtain an optimal and smooth result, post-treatment techniques such as polishing, tumbling or shot blasting should be used for surface finishing. Heat treatments can also be applied to reinforce the properties of the final parts.
Main Applications
Regardless of the process used, 3D printed parts made of aluminum alloys offer interesting properties for a multitude of industries. In addition to their good chemical resistance and light weight, they have one of the best strength-to-weight ratios of all metals. The most common applications for this metal include the manufacture of short series or prototypes. Others are related to structural lightweighting or heat transfer, as in the case of customized heat exchangers. Combined with silicon and magnesium, it is the choice par excellence of many players in the aerospace and automotive industries, where the demands are really high.
In the automotive sector, Porsche 3D printed aluminum pistons for its flagship model, the GT2 RS. The use of metal additive manufacturing enabled the company to obtain up to 30 hp more power from the 700 hp twin-turbo engine, while improving the vehicle’s efficiency and performance. Mercedes-Benz, meanwhile, is 3D printing aluminum replacement parts for its line of trucks and cars to ensure greater road safety.
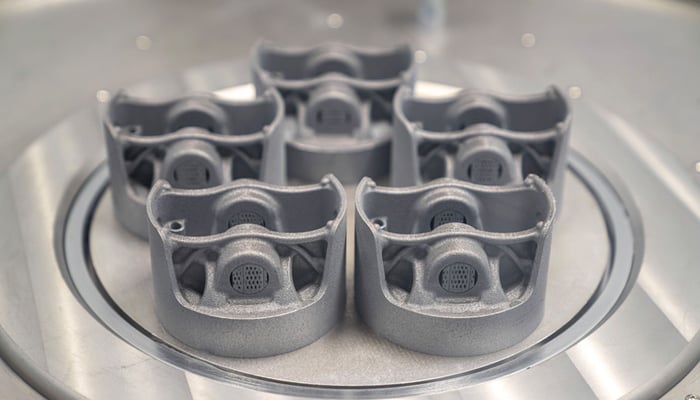

Pistons 3D printed in aluminum (photo credits: Porsche)
The aerospace industry is also not lagging behind in the implementation of aluminum 3D printing in its business. Airbus, for example, manufactured parts using aluminum alloys for its A350 XWB and other aircraft, as well as for its communications satellites. Boeing has also turned to metal additive manufacturing to create aluminum parts for its airplanes, satellites and helicopters. This cutting-edge technology can result in lighter structures and allow aircraft to travel farther on less fuel.
Aluminum Manufacturers on the 3D Printing Market
As mentioned, the material is mainly found in powder form, but also in wire for certain technologies. As of today, there are only two companies developing aluminum in filament form for FDM 3D printing, and they are The Virtual Foundry (Aluminum 6061 Filamet™) and Zetamix (alumina-based, i.e. aluminum oxide).
On the other hand, the use of this powder material is much more widespread. Today there are many companies dedicated to the development of aluminum powder, such as Elementum 3D, APWorks, Uniformity Labs, ECKA Granules, Equispheres or Constellium, among others. It is also worth noting that some 3D printer manufacturers such as EOS also develop their own powdered materials.
Do you have experience with aluminum 3D printing? Let us know in a comment below or on our Linkedin, Facebook, and Twitter pages! Don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly Newsletter here, the latest 3D printing news straight to your inbox! You can also find all our videos on our YouTube channel.
*Cover Photo Credits: 3dsla.ru







Hallo, I would like to ask if you can print 3D printing of metal and aluminium. Would it be possible to send us an offer if I will send you drawing in PDF? Thank you. Andrea Alscherova