NIOSH Releases Report Establishing 3D Printing Safety Guidelines

The rapid advancement of 3D printing technology has revolutionized various industries, offering unprecedented opportunities for innovation and product development at rapid speeds. This technology has also transcended the boundaries of industrial settings, finding its way into schools, libraries, small businesses, and homes. As its popularity in these non-industrial environments continues to rise, it is crucial to address potential health and safety concerns associated with the 3D printing process.
Recognizing this growing need, the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) conducted an in-depth evaluation of the health and safety risks associated with 3D printing in non-industrial workplaces. Their findings are compiled in the recently released investigatory report, “Approaches to 3D Printing: A Guide for Makerspace Users, Schools, Libraries, and Small Businesses,” which seeks to equip users with helpful insights and recommendations to reduce these risks.

As 3D printing makes its way into more environments, including jobs, it is important to develop safety guidelines.
The report emphasizes understanding the various stages of the 3D printing workflow, each presenting its own potential hazards. From meticulous pre-printing tasks like printer maintenance and cleaning to post-printing activities like removing support structures and applying finishing touches, individuals involved in the process can be exposed to a variety of materials that may potentially pose health risks.
What Is Inside the NIOSH Safety Guidelines?
One crucial aspect of the NIOSH report is the identification of hazards arising from exposure to materials emitted during the printing process. Research suggests that 3D printers emit ultrafine particles and volatile organic compounds, which can be harmful to the respiratory and cardiovascular health of individuals in close proximity to them for extended periods. The report highlights the importance of understanding the specific emission characteristics of different 3D printing materials and technologies to effectively manage these exposure risks, specifying hazards for each type of printer.
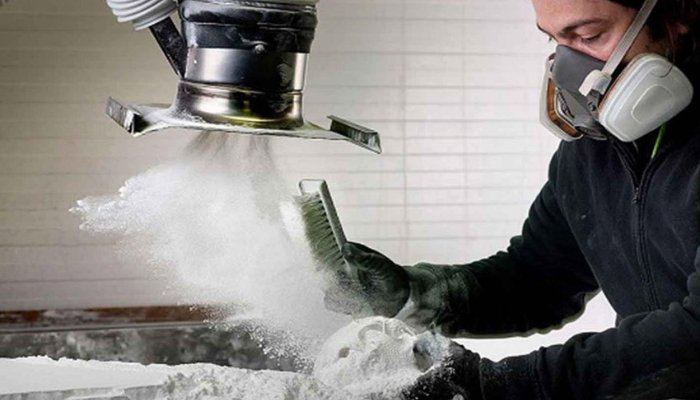

Personal protective equipment should be worn during post-processing, as powder can be dispensed into the air (photo credits: Protolabs)
Alongside emissions, the report dives deeply into other risks generated by 3D printing, covering topics such as solvents, heat, moving parts, lasers, and noise. To better navigate the potential dangers associated with 3D printing in non-industrial settings, the NIOSH report emphasizes the need for a tailor-made risk management plan. This plan should be unique to each workspace environment, considering its specific needs and circumstances. Ideally, according to NIOSH, it should encompass a detailed approach to 3D printing safety, covering four main goals.
Firstly, the identification of potential hazards, as risks can be identified at each stage of the 3D printing process, from preparation and printing to post-processing. Next, the report encourages the implementation of control measures to minimize these risks once they are identified. After, NIOSH recommends the provision of training, helping to spread awareness of risks to increase safe practices and procedures. Lastly, regular monitoring and evaluation of the effectiveness of implemented procedures and control measures, to ensure ongoing safety and identify areas for improvement.
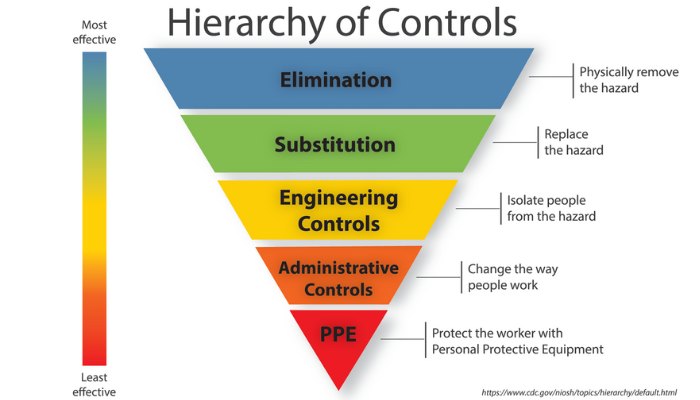
Photo Credits: The National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health
As 3D printing continues to be widely adopted, the NIOSH report offers a critical foundation for proactive safety measures across various sectors. By identifying safety gaps, NIOSH has helped to ensure the safety of workers, businesses, and consumers. To read the report, click here.
What do you think of the recommendations given in this report released by NIOSH? Let us know in a comment below or on our LinkedIn, Facebook, and Twitter pages! Don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly newsletter here, the latest 3D printing news straight to your inbox! You can also find all our videos on our YouTube channel.