The Role of 3D Printing in the Luxury Goods Sector

The global luxury goods market is experiencing a rapid post-pandemic recovery and could reach €380 billion by 2025, according to a report published by the Italian luxury goods manufacturers’ foundation, Fondazione Altagamma, and strategic consulting firm Bain & Company. In this growing market, the role of 3D printing in the luxury sector is becoming increasingly important. From accessories to eyewear to haute couture pieces to sports car components, additive manufacturing has a lot to offer to the demanding luxury market.
Companies such as Dior, Louis Vuitton, Bentley and Porsche have already dared to take the plunge, persuaded by the many benefits 3D printing technologies have to offer. Yet, many other well known brands still refuse to make use of the innovative option. Why are those companies still holding back from these opportunities? How can additive manufacturing be used in the luxury sector anyway? To get to the bottom of that question, we’ll look at three of the luxury industry’s fundamental pillars: cars, jewelry and haute couture, to learn a little more about how luxury companies are implementing new technologies and the value they’re getting from doing so.
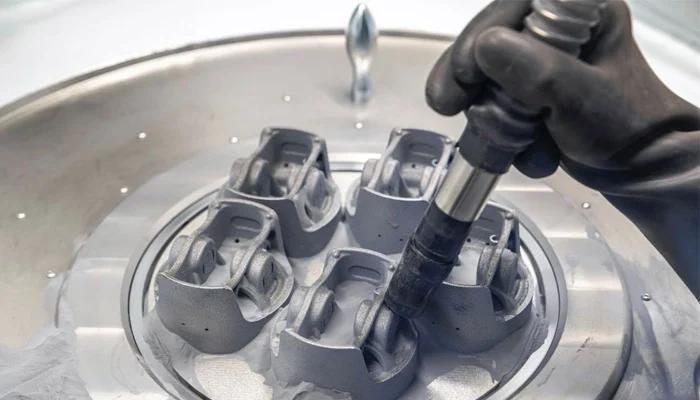

Pistons made by Porsche using additive manufacturing (photo credits: Porsche)
3D Printing And Luxury Cars
Many luxury and sports car manufacturers tend to demand very high standards. This category of car manufacturers needs parts that are both visually striking and extremely durable. Additive manufacturing is the perfect choice to meet these expectations. The technologies make it easy to manufacture complex shapes and minimize weight by applying material only where it is really needed. In addition, 3D printing offers a cost-effective way to produce small volumes.
3D Printed Applications in the Automotive Sector
An important benefit of the use of 3D printing technologies in the automotive sector is the ability to print much more customized components from the factory, giving the car unique performance characteristics. British luxury car manufacturer Bentley is one of those who have already successfully implemented it. Consumers spend thousands of dollars each year to customize their vehicles, and manufacturers can benefit from that by using additive manufacturing to their advantage. Another application of 3D printing is the creation of hard-to-find or obsolete parts. There are a growing number of vintage car collectors and manufacturers are working to restore and preserve certain models that are considered gems in the eyes of collectors. Besides those two possibilities, another option for the use of additive manufacturing is becoming more and more popular: 3D printed cars. Perhaps one of the best examples here is Divergent, a California-based high-end sports car company that makes ultra-lightweight chassis and has an ambitious goal to design all of its car parts using 3D technologies. But Divergent is not alone: 1016 Industries have also made 3D printing available to luxury brands such as McLaren, offering optimized final parts.
“Our focus for this project was exploring how we could employ 3D printing in the automotive world, and the results creating these McLaren 720S parts are impressive. The 3D-printing process has not only allowed us to manufacture faster and more efficiently, but we’ve also improved quality. The 3D technology has allowed each 1016 Industries part to be even more accurately made, with each part printed in real scale to validate our CAD and CFD work.” – Peter Northrop, founder of 1016 Industries.
In addition to that, 3D technologies can provide fully functional prototypes for rigorous testing and simulation, tooling for limited edition components, and low-volume custom production parts for final use in vehicles.
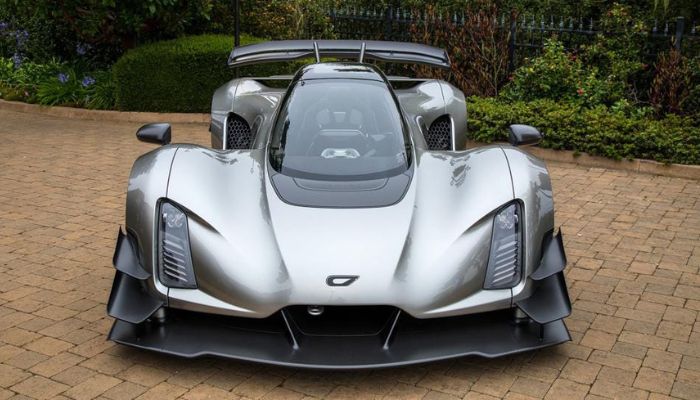

The Czinger 21C luxury car from Divergent 3D (photo credits: Divergent 3D)
The Most Used Technologies
There are several 3D printing technologies used to produce automotive parts, depending of course on the end application. For example, Porsche uses Powder Bed Fusion to create the pistons for the 911 GT2 RS from metal powder. British luxury car designer Vital Auto uses SLA technology, also known as stereolithography, to produce other automotive parts such as air vents or door seals. Another of the most widely used technologies in this field is FDM technology, which is mostly used in the prototyping phase, as it is a fast and efficient way to physically lay out components before the final production.

The Aston Martin Callum Vanquish 25 will feature several 3D printed parts (photo credit: Makerbot)
The Benefits of 3D Printing in the Automotive Sector
3D printing shortens lead times: Any part can be available in a matter of days or hours, even the scale model of a complete car, and at a lower cost. In addition, 3D printing makes it possible to work with thinner sections, more customized and tailored designs, and to test different versions quickly and cheaply. One example is Bugatti, which 3D printed its eight-piston monoblock brake caliper in titanium, saving money and improving performance by reducing the weight of the part and making it stronger.
Additive Manufacturing and Haute Couture
Many of the most exclusive designers and companies in the fashion world have opted for 3D printing technologies to make all kinds of clothes: dresses, bags, shoes, etc. If you take a look at some of the most important and luxurious events in the fashion industry, such as the Cannes Film Festival, the Met Gala or many of the world’s most important fashion shows, it is very likely that someone is wearing a piece of 3D printed clothing.
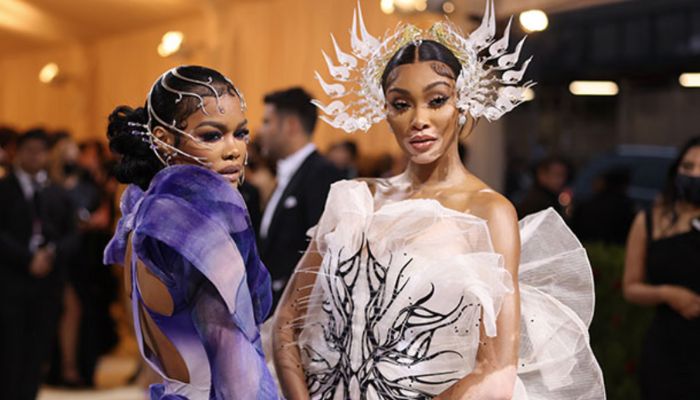

Teyana Taylor and Winnie Harlow in couture dresses by Dutch designer Iris Van Herpen (photo credits: John Shearer)
3D Printing Applications in Fashion
In the world of haute couture, 3D printing plays a very important role because it enables a freedom of design that isn’t possible to have when using conventional manufacturing methods. With 3D technologies, we can print different garments: one of them is shoes, as in the case of high-end shoe designer Annie Foo. By scanning the customer’s foot, the designer gets pieces that are totally adapted to their physiognomy while offering organic shapes. In addition to designers making custom-made garments for each client, there are also high-end companies that have already 3D printed shoes, such as Balenciaga, which costs around $3,250.
There are also some 3D printed garments, such as those made by Iris Van Herpen, that’s designs transcend boundaries and in which 4.0 technologies and traditional craftsmanship are combined. Iris’ visionary designs fuse pioneering techniques and luxurious materials, often evoking a pre-war feeling.
There are also high-end 3D printing companies that focus entirely on the fashion and luxury sector, such as VOJD Studios, which works with brands such as Kenzo, Acne Studios, Louis Vuitton, Alexander McQueen and Carolina Herrera and helps them integrate 3D printing into their collections. Other companies, such as Dior, have used 3D printing to create thousands of prototypes and exact replicas of their collections to decorate their stores, such as the impressive 3D printed collection for the famous Dior Gallery in Paris.
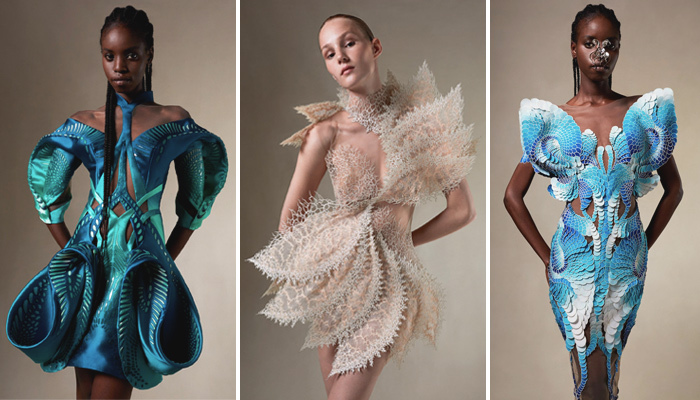

Models from Iris van Herpen’s Earthrise collection, where 3D printing is used (photo credits: Iris van Herpen)
The Most Used 3D Printing Technologies in the Luxury Sector
Currently, designers and creators are looking for materials that are rather soft and will recall the appearance of leather or fabric. Those vary depending on the garment to be printed. In the case of rigid garments, it is possible to use different printing technologies such as SLA, LCD, DLP or SLS. This allows the fashion industry to create complex designs with a lot of detail, often for fashion shows. For more flexible garments, such as those created by Israeli designer Danit Peleg, TPE is often used. TPE is an elastomer that can be stretched to the breaking point and has a high coefficient of friction, making it very flexible, so the results are very similar to a textile mesh. For these elastic parts, FDM is probably the most used technology. Finally, the material jet process is particularly popular because it adds realism to creations and allows for the addition of color.
What Are the Pros and Cons of Additive Manufacturing in Luxury Fashion?
In a cutting-edge industry like fashion, combining the latest trends with the latest 3D printing technology allows companies to differentiate themselves from their competitors. 3D printed designs are sustainable, more environmentally friendly and personalized. Customization has become a key trend that is present in all luxury sectors. Consumers of these products want unique garments, imagined just for them, which explains the success of brands that offer custom products. For Danit Peleg, who uses 3D printing in his production process, the main advantages of 3D printed fashion are individuality, flexibility and durability.
“There’s zero production waste – no scraps or unwanted clothing in the shops. If you get tired of a garment, you can simply melt it and make a new one” Danit Peleg explains.
One of the main disadvantages of 3D garments is their rigidity, which limits people’s mobility. Currently, cotton and silk are much more comfortable to wear. It would be interesting to find solutions to introduce more flexible materials or explore the concept of 3D printed knitwear.
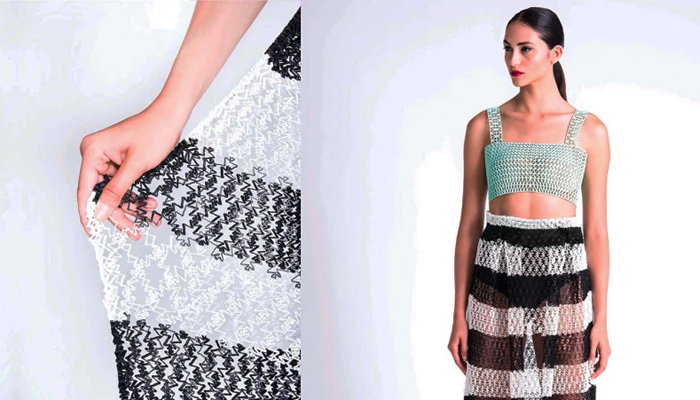

3D printed clothes have a different texture than conventional products (photo credit: Danit Peleg)
3D Printing and Jewelry
Jewelry making, as an economic activity, dates back to ancient Egypt, 3,000 to 5,000 years ago. The jeweler has witnessed and played a leading role in successive technological innovations, century after century. But in the long history of jewelry, no technical advance has had as much impact as additive manufacturing. It offers jewelry designers a wide range of possibilities, including customization, aesthetics, and production speed. That’s why world-renowned companies such as Cartier and Tiffany & Co. have integrated 3D printing into various stages of the production process, from prototyping to post-processing to lost-wax processes.
How Can We Use 3D Printing in Jewelry?
3D printing is used in various ways in the jewelry industry. One of the most typical applications is prototyping. Additive manufacturing allows the jeweler and customer to visualize the part, albeit in a different material, before creating the final piece. This helps refine the design, reduce the time needed for modifications and eliminate errors in the final design. On the other hand, we have what are called indirect manufacturing methods. In these cases, 3D printing is used as a fast, accurate and efficient way to produce a basic model of the part. The model is then used to make a mold, which is ultimately used to obtain the final part by casting and solidifying the final material of the part.
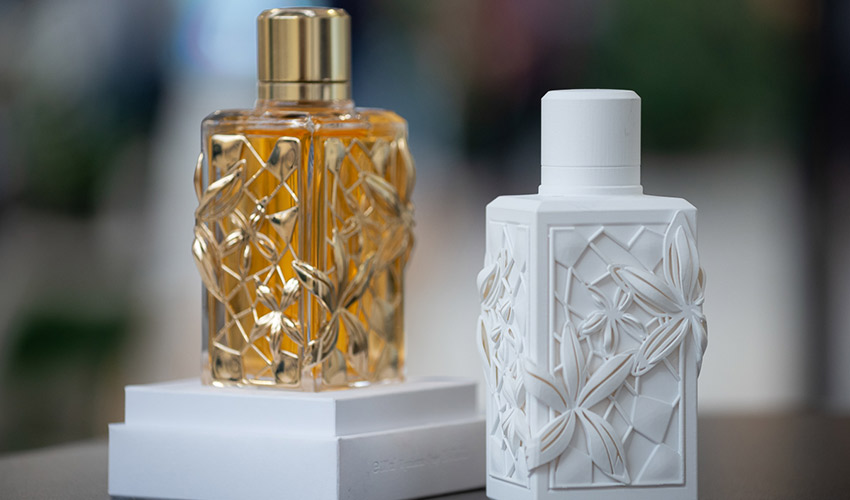
Another of the processes used is that of lost wax casting, which allows for much more complex shapes. This is a method in which molten metal replaces a wax model placed in a mold by melting it. Jewelers can now 3D print this model, giving them more freedom in terms of geometry. It is then possible to produce metallic accessories for perfumes, or aesthetic and technical accessories for leather goods.
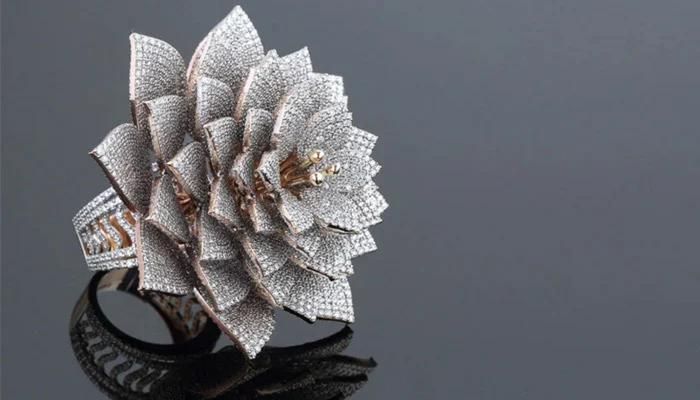

The ring that broke the world record of 7,801 diamonds! was designed using a 3D printed mold (photo credits: Imaginarium)
The Most Used Technologies to Create 3D Jewelry
If there is one additive manufacturing technology that will be of extraordinary importance to the jewelry industry, it is the one that allows the construction of metal objects, such as laser fusion. Other companies, such as EAC, opt for Metal Binder Jetting, which allows a higher level of quality and productivity, guaranteeing a better finish of the part. Among the most used technologies are stereolithography, valued for the level of detail it offers, FDM and Polyjet technology. Stereolithography and FDM are technologies commonly used for printing prototypes in hot melt materials, which are used in the manufacture of jewelry parts by lost wax casting.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Additive Manufacturing in Jewelry
Thanks to additive manufacturing, jewelers can improve their efficiency and productivity in their work, because while the printer performs its function, they can focus on other tasks. In addition, thanks to it, it is possible to obtain several pieces with high quality and definition of details, especially in the case of complex and complicated designs. Despite the many advantages, not everything is rosy, and the acquisition of a 3D printer involves an investment in time to learn how to model, as well as money to acquire this new technology.
With 3D, there are no limits to creativity. Additive manufacturing allows us to manufacture and duplicate any small part, to print and metalize parts in series. We are able to create, polish and metalize parts of previously unthinkable complexity. With this new technology, we can meet any type of demand. Additive manufacturing allows our designers and customers to set no limits on the design of their accessories,” said Patrick Chouvet, CEO of EAC.
The Future of 3D Printing in Luxury
As discussed earlier, the luxury market is growing and represents a high value. This makes it a key target market for 3D printed clothing, accessories, cars, etc. Luxury customers, especially millennials, are increasingly looking to express their own individuality through material goods, such as clothing or cars. Therein lies the real appeal of 3D printed products: they offer great customization and uniqueness, so designers, such as Iris van Herpen, who use additive manufacturing processes, have the opportunity to market their products to an increasingly affluent market.
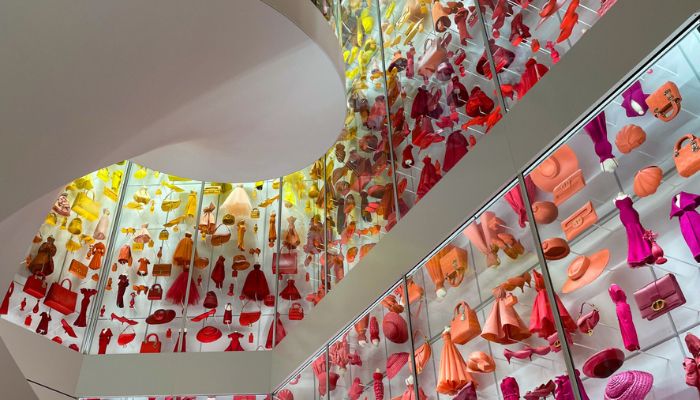

In the Dior Gallery in Paris, thousands of pieces have been reproduced using 3D printing (photo credits: Dior)
In addition, specific customers such as the before mentioned millennials or specific markets such as the Chinese market are always open to technological advancements and sustainable clothing. Therefore, it is very likely that their predisposition to purchase 3D printed luxury goods is positive. However, there is still a long way to go. For example, in the fashion world, 3D printing technologies are not mature enough. We are getting unique designs, but their performance is inferior to that of traditionally made garments. Will we be able to overcome this obstacle?
What do you think about the use of 3D printing in the luxury sector? Let us know in a comment below or on our LinkedIn, Facebook, and Twitter pages! Don’t forget to sign up for our free weekly Newsletter here, the latest 3D printing news straight to your inbox! You can also find all our videos on our YouTube channel.